TRaCE Partnership: Shaping the future of hydrogen fuel cells with silicon
The original article can be found here: https://trace.org.au/shaping-the-future-of-hydrogen-fuel-cells-with-silicon/
24 January, 2025
Siltrax is revolutionising hydrogen fuel cells using silicon-based bipolar plates
The global push for the energy transition remains an uphill battle, with fossil fuels continuing to dominate as the primary energy source despite their environmental toll. Hydrogen, however, has emerged as a promising alternative. As a clean fuel, it can power everything from cars to industrial systems, with the added advantage of producing only water as a byproduct when used in hydrogen fuel cells, a device that generates electricity by combining hydrogen with oxygen.
However, the commercialisation of hydrogen fuel cells has been slow due to the high costs associated with this technology.
One of the major cost drivers is the bipolar plate, the core component of hydrogen fuel cells. Traditionally made from stainless steel, titanium, or aluminium, these materials are difficult to machine and highly prone to corrosion, requiring expensive coatings and treatments. Meanwhile, graphite plates, an alternative, are brittle, and heavy, making them unsuitable for mobility applications. This has left the hydrogen fuel cell industry grappling with a need for a better, more cost-effective solution that can cater to a wide range of applications.
In response, Siltrax has developed ultra-thin, low-cost silicon-based plates that replace traditional materials in hydrogen fuel cells.
The solution: Silicon-based bipolar plates
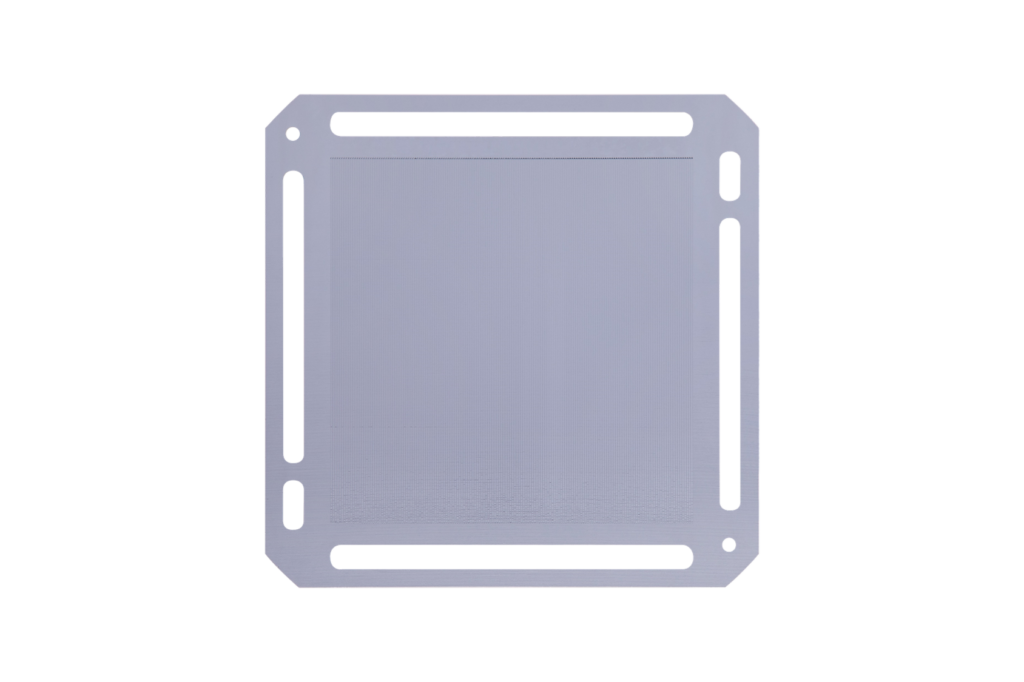
Siltrax’s founders have been world leaders in silicon technology for over a decade and have built a deep expertise in solar panels. The company’s technology has been developed by Dr. Zhengrong Shi, a renowned solar entrepreneur, and Dr. Jim Zhu, a semiconductor expert. They wanted to integrate their knowledge in the hydrogen industry.
“This project is incredibly exciting for us as it represents a full-circle moment – leveraging our expertise in photovoltaic technology to tackle the hydrogen sector, applying our knowledge in a whole new domain,” says Dr Zhengrong Shi.
Siltrax’s efforts have culminated in the creation of a revolutionary silicon-based bipolar plate, offering the following features:
– Lightweight and compact, offering high power density for both weight and volume.
– Strong performance with high current output.
– Long-lasting use, thanks to the inherent stability of silicon.
This combination of efficiency, power, and durability makes it a promising solution for the hydrogen fuel cell industry.
Additionally, silicon’s natural abundance and environmental advantages over precious metals make it a sustainable choice for the hydrogen economy.
The Trailblazer for Recycling and Clean Energy (TRaCE) Collaboration
Siltrax has partnered with UNSW renowned experts on hydrogen fuel cells, Dr. Quentin Meyer and Professor Chuan Zhao, to validate its silicon-based bipolar plate technology through the TRaCE Lab to Market Fund program.
“This R&D project, supported by TRaCE’s Lab to Market Fund, will test the innovative silicon-based technology in real devices and assess the performance of the silicon bipolar plates, marking the first independent academic evaluation of the technology,” explains Dr. Quentin Meyer.
The collaboration combines Siltrax’s expertise in design and prototyping with UNSW’s leadership in hydrogen research. “UNSW and Siltrax combine the best of both worlds, combining state of the art manufacturing with world-leading electrochemistry and fuel cell expertise. Truly, it’s a very exciting project for us, and I am eager to see where this takes us! The TRaCE program provides a great platform and outstanding support to both teams”, adds Prof Chuan Zhao.

With significant funding secured, Siltrax is now focused on scaling and commercialising its solution both in Australia and globally.
This partnership also marks a full-circle moment for Siltrax’s founders, who are alumni of UNSW, where their journey in silicon technology began.
Driving decarbonisation in heavy transport and aviation
“The potential decarbonisation impact of this technology is significant. By lowering costs, improving accessibility, and leveraging the environmental benefits of hydrogen, these fuel cells will help drive the transition from fossil fuels to a hydrogen-based economy,” says Fred Qi, director of R&D at Siltrax.
This project is particularly focused on hard-to-decarbonise sectors like heavy transport, shipping, and aviation, which will hugely benefit the environment. Aviation, for example, accounts for 5% of Australia’s CO2 emissions and has seen fewer electrification efforts. By supporting this sector, the project will contribute to Australia’s path toward a net-zero economy.
Additionally, using silicon, a more abundant and less environmentally harmful material than precious metals, reduces the environmental impact of mining and processing.

Siltrax’s ambitions extend far beyond Australia. The company is actively exploring opportunities in Southeast Asia, Europe, and the United States. Meanwhile, Australia remains its first target market, with plans to address challenges like decarbonising heavy road transportation and providing clean energy solutions for off-grid communities.
As Siltrax moves towards commercialisation, TRaCE will continue to provide support through its ecosystem, opening doors to new partnerships and helping scale this groundbreaking technology.
"*" indicates required fields